INDICATIONS
Nplate® is a thrombopoietin receptor agonist indicated for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in adult patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) who have had an insufficient corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy. Nplate® is indicated for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with ITP for at least 6 months who have had an insufficient response to corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or splenectomy.
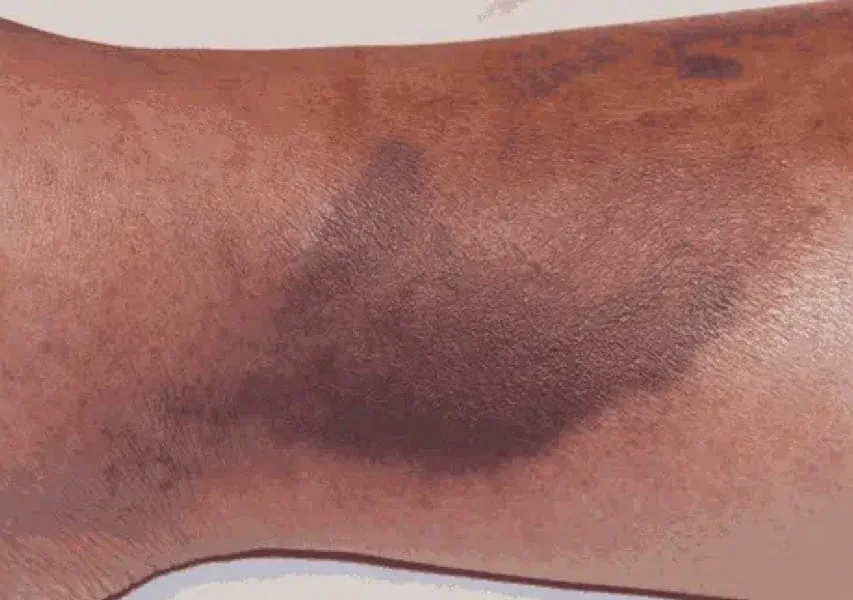
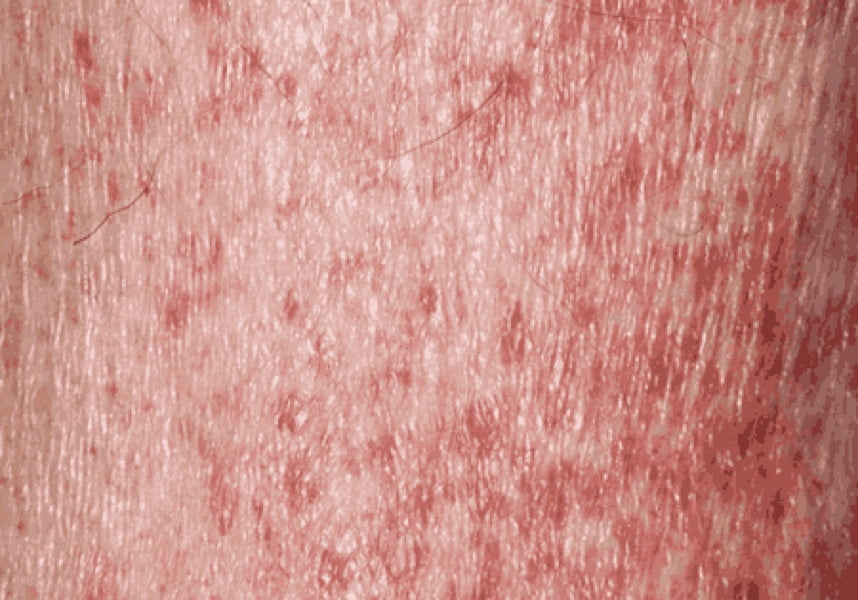
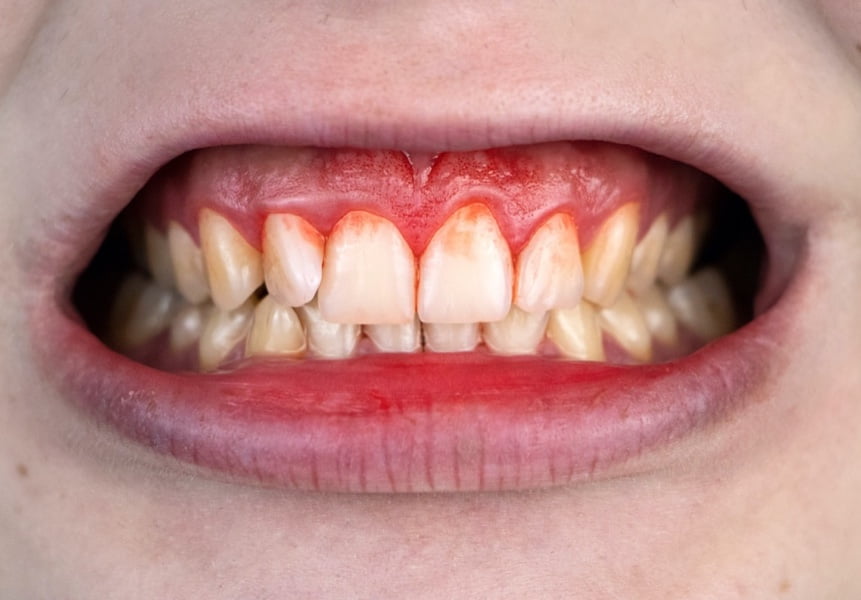
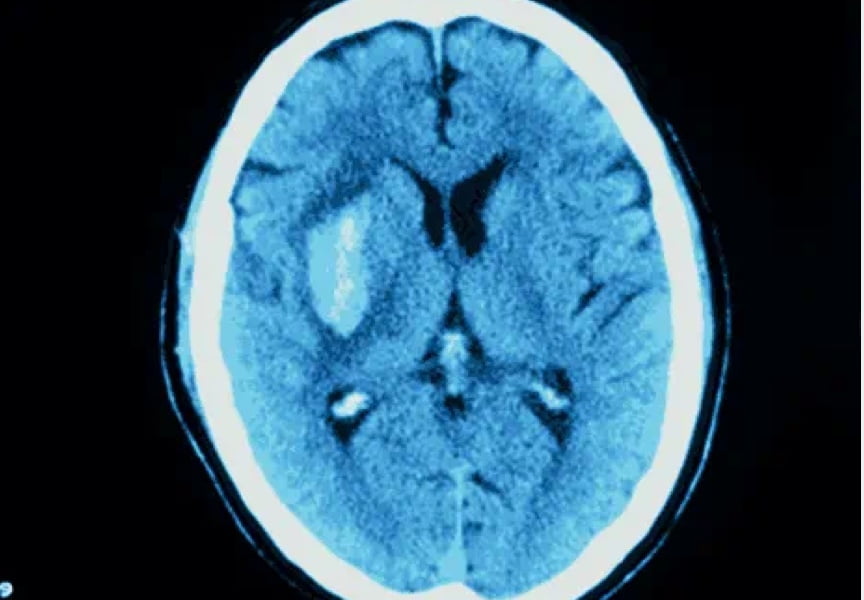
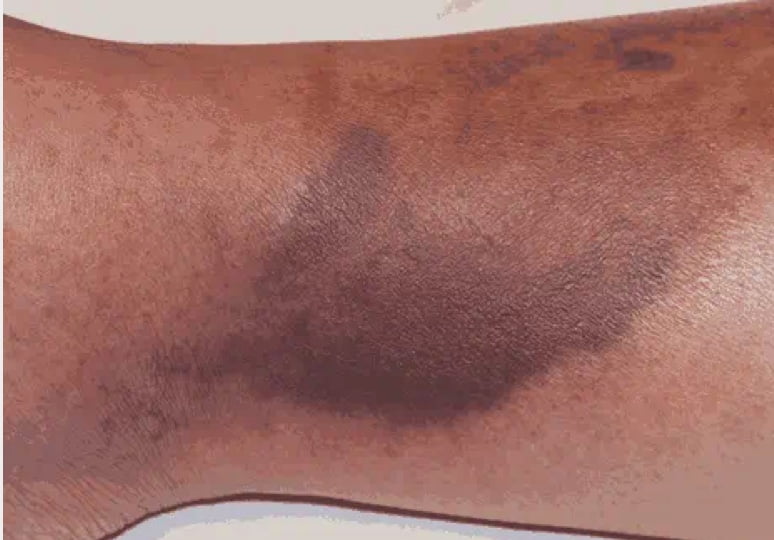
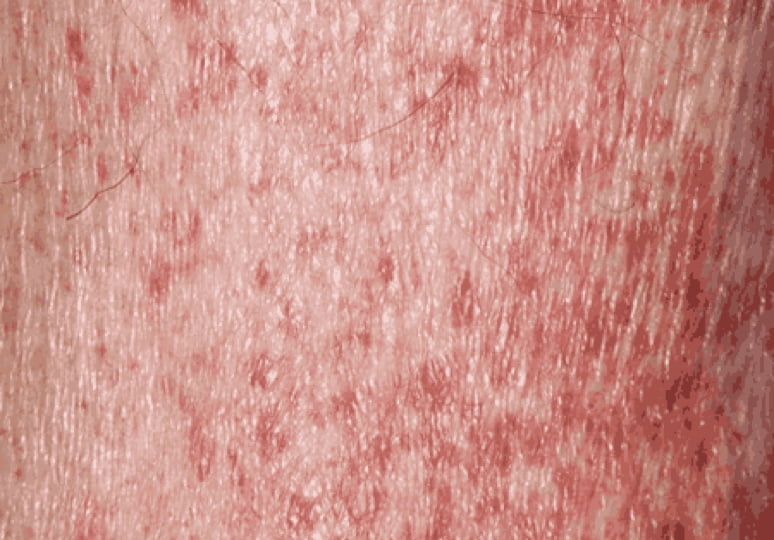
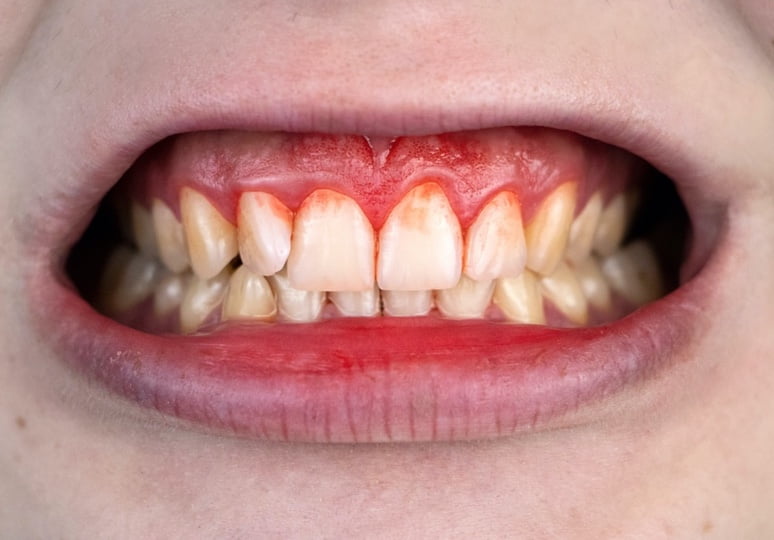
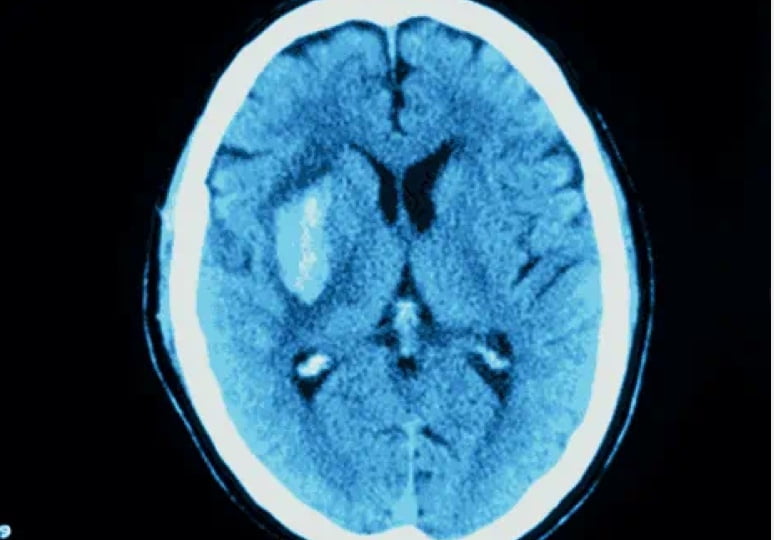
Nplate® is not indicated for the treatment of thrombocytopenia due to myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or any cause of thrombocytopenia other than ITP. Nplate® should be used only in patients with ITP whose degree of thrombocytopenia
and clinical condition increase the risk for bleeding. Nplate® should not be used in an attempt to normalize platelet counts.